Feature ArticleCommon Reasons for Damages in BPHEs- (2) Corrosion
reads
Brazed plate heat exchanger is formed with chevron plates and vacuum brazed with copper, it contains very compact and special structure. Two fluids can perform high efficiency heat exchange with very little temperature difference, it is also corrosion resistant, pressure resistant, compact, high efficient. It is widely used in HVAC, hydraulic cooling, heat recovery…ect, and acting as a very important role in energy saving and carbon emission reduction in major industries.
Brazed plate heat exchanger normally has long lifetime under suitable working conditions, however we still need to be cautious about the followings that may cause rare damages. Kaori’s BPHE team has more than 30 years of experience in helping system designers and users to use BPHE properly, so the lifetime is maximized, making it economical and satisfactory for customers.
Corrosion
Common characteristics
Normally there is no deformation on the heat exchanger, but abnormal color can be spotted (at outside or inside the heat exchanger, commonly copper oxidation). Sometimes internal leakage takes place, and need to be investigated through cutting and disassembling the heat exchanger.

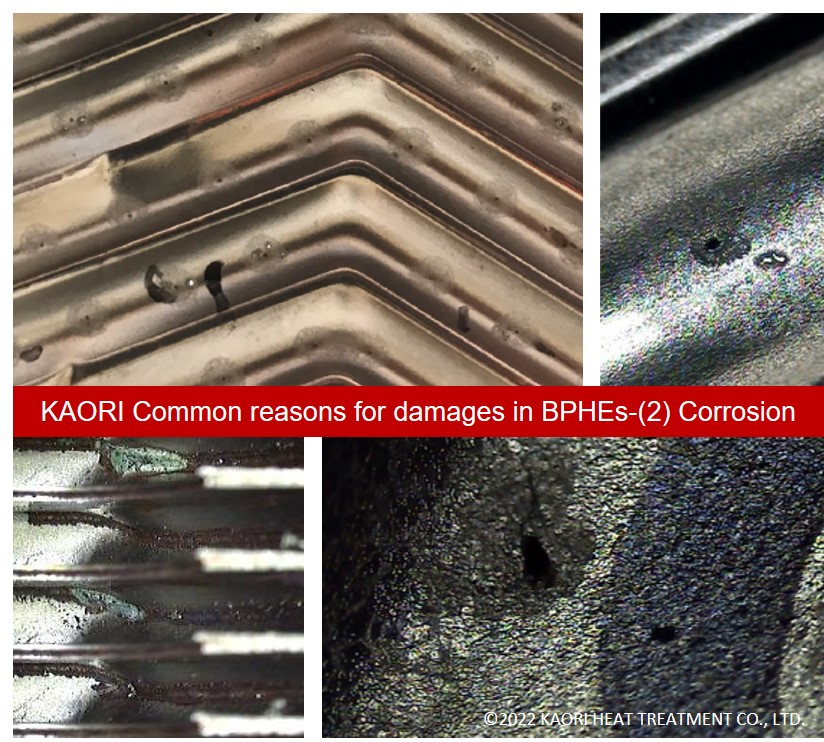
Common Reason
- Electrochemical Corrosion: Pure water with low electrical conductivity belongs to this group (ex: EC < 10 µS/cm)
- Chemical Corrosion: ex: PH>8 or PH<6、Cl-(>50ppm)、SO42-(>30mg/L)、NH4+(>0.1mg/L)
- Microbial Corrosion: This is rare, reasons need to be investigated
- Effect of Velocity: Including Erosion and cavitation
- Stress Corrosion: Stress with high temperature also speed up oxidation
- Others:
- Refrigerant corrosion
- Normally refrigerant and refrigerant are not corrosive, however when system vacuum is poor due to piping and assembly, refrigerant will oxidize with oxygen and water molecule, it is possible to form acidic material like fluorine or chlorine.
- Welding of connections (copper or argon), flux residue or other oxidized material due to high temperature can also cause corrosion on refrigerant side.
- Chemical reaction between POE refrigerant oil with water (oxygen), this forms oil congestion and acidification, high temperature also speed up the corrosion.
- Prevention
- Check and replace refrigerant desiccant filter.
- Fill up connections with nitrogen during welding to perform oxygen free welding, perform cleaning after welding
- Corrosion caused by other fluids
- When one or more corrosion are present.
- Be cautions of the affect to stainless steel and copper.
- The damage of chromium oxide on stainless steel, for example, damages, scratch and pore made to the plate by mechanical operation.
- Prevention
- Avoid using improper fluids
- Avoid corrosion causes
- Back flush cleaning must be thoroughly performed to avoid residue
- Refrigerant corrosion

