Feature ArticleCommon Reasons for Damages in BPHEs- (4) Stress
reads
Brazed plate heat exchanger is formed with chevron plates and vacuum brazed with copper, it contains very compact and special structure. Two fluids can perform high efficiency heat exchange with very little temperature difference, it is also corrosion resistant, pressure resistant, compact, high efficient. It is widely used in HVAC, hydraulic cooling, heat recovery…ect, and acting as a very important role in energy saving and carbon emission reduction in major industries.
Brazed plate heat exchanger normally has long lifetime under suitable working conditions, however we still need to be cautious about the followings that may cause rare damages. Kaori’s BPHE team has more than 30 years of experience in helping system designers and users to use BPHE properly, so the lifetime is maximized, making it economical and satisfactory for customers.
Stress
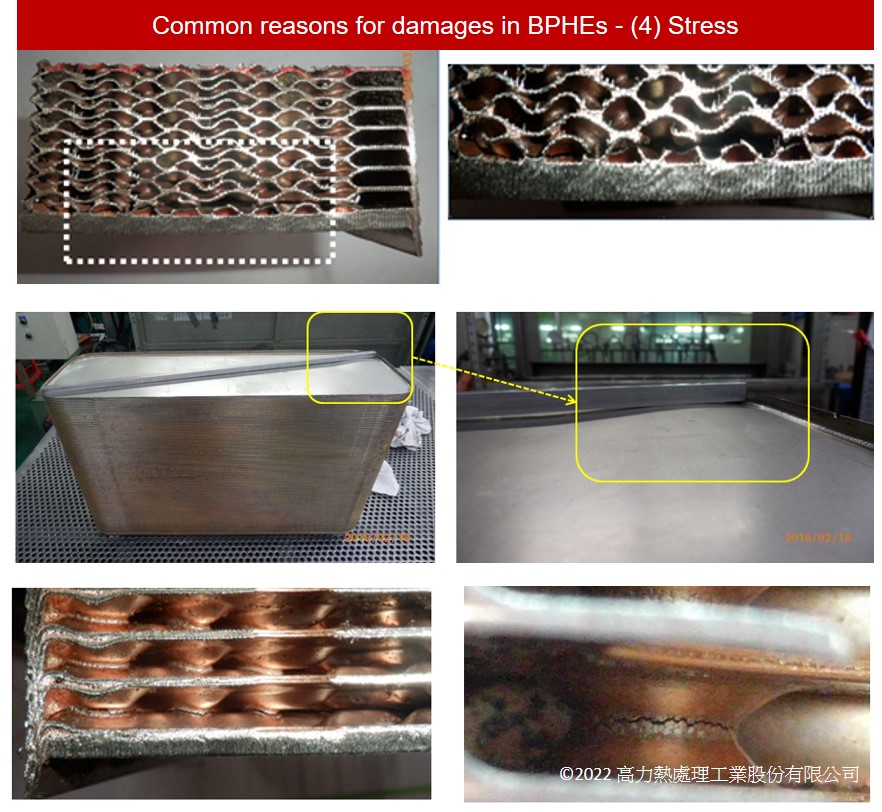
Stress damage takes place when pressure is too high or pressure repeats, including water hammer and sudden pressure, this can cause disruption in the plate. Also in some cases where high temperature difference or corrosive elements are present in the fluids, it speeds up the damage.
Common characteristics
Most of stress damage are located near the connections or the bottom of the heat exchanger.
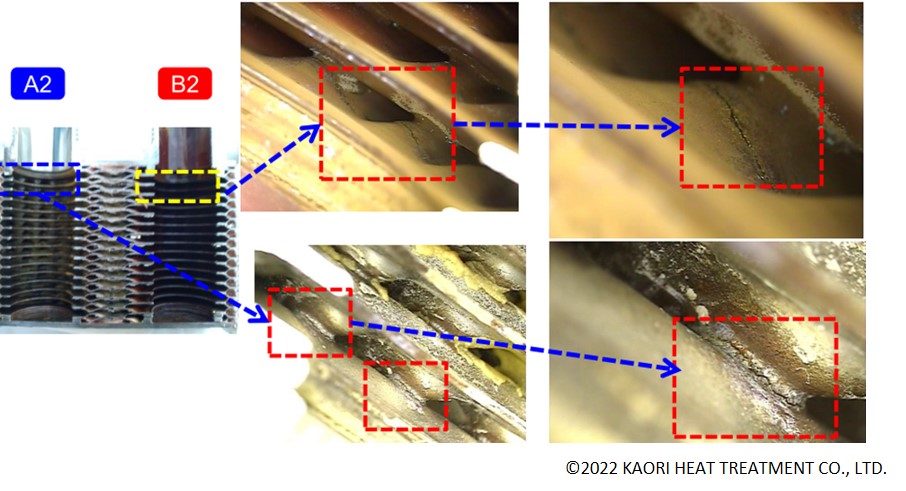
Other types (Stress corrosion)
Due to fluid temperature and corrosive elements, when stress is added, plate damage speeds up.
Combining all possibilities of the damages, we can conclude damages are not caused by one single reason. Normally we need consider the working condition and how it is used to determine the cause of the damage. We hope this information will provide better understanding of BPHE, and better use this product for your application.
Common reasons for damages in brazed plate heat exchangers series of articles
- Common Reasons for Damages in BPHEs- (1) Scaling
- Common Reasons for Damages in BPHEs- (2) Corrosion
- Common Reasons for Damages in BPHEs- (3) Freeze

